FSI Urges Unified Global Approach to Regulate Stablecoins
In addition, the FSI report tackles the problems of the diverse stablecoin definition and classification in different countries. This fragmentation of the regulatory fields in the financial sphere may cause serious issues for integrated systems, which threaten general financial stability
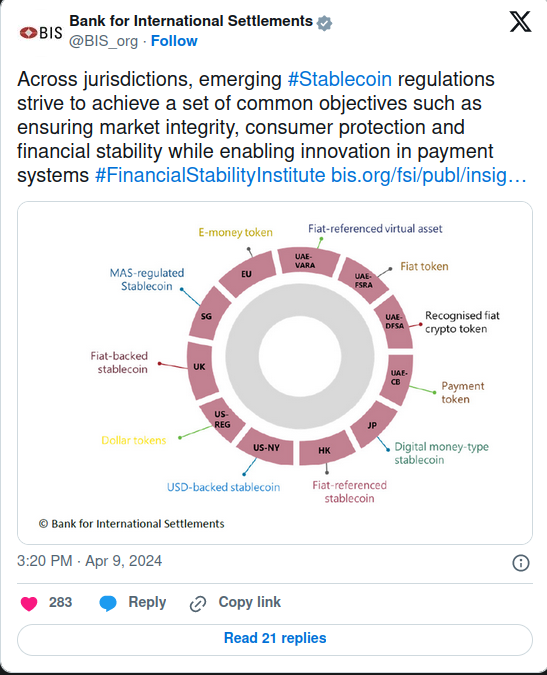
Various Responses to Stablecoin Regulation
The FSI's call for a unified regulatory method is due to the varying approaches adopted by countries in regulating stablecoins. Moreover, stablecoins have received varying levels of regulation across the globe. In 2023, the UK legalized stable assets as a means of payment, and the EU brought the Markets in Crypto Assets Regulation (MiCA) to supervise stablecoin issuers and service providers.
Japan, in addition, has started regulating the stablecoin market, and a stablecoin bill is being considered in the United States. This diversity of responses, as a result, points out the necessity for a unified approach to prevent fragmentation and a possible systemic threat.
Risk of Regulatory Fragmentation
In addition, the FSI report tackles the problems of the diverse stablecoin definition and classification in different countries. This fragmentation of the regulatory fields in the financial sphere may cause serious issues for integrated systems, which threaten general financial stability.
The report suggests that even if the core regulatory standards are the same in many countries, differences arise out of the various design features of stablecoins and the risks associated with them. Such anomalies may lead to regulatory arbitrage, which is the abuse of differences in regulation to pose a danger to the stability of the financial system.
Promoting an Integrated Financial System
The relevance of a harmonized regulatory framework and global adoption is also highlighted in the report. Such an approach is important not only in managing stablecoin risks but also in promoting fair competition in the digital asset ecosystem. In addition, the FSI highlights the importance of stablecoins' interoperability with central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and other digital assets, as it would contribute to a more coordinated financial system.
An important aspect here is the participation of international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in forming the universal standard of stablecoins.
Comparative Analysis of Regulatory Frameworks
The FSI report provides a detailed analysis of the regulatory frameworks for stablecoins across seven jurisdictions, encompassing 11 different authorities. This comparative study aims to identify common trends and practices among the various regulatory measures. Key areas such as licensing, reserve asset management, redemption rights, capital adequacy, consumer protection, governance, risk management, cybersecurity, and compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and countering the financing of terrorism (CFT) standards are covered. The analysis underscores the evolving nature of the stablecoin market and the corresponding regulatory responses, underscoring the necessity of a globally coordinated approach to regulation.